In Society
Gidon Eshel: The Diet Disruptor
Dr. Gidon Eshel is not the kind of climate scientist who limits his attention to melting glaciers or atmospheric physics. Trained as a physical oceanographer at Columbia University and later a postdoctoral researcher at Harvard, Eshel has spent the past two decades changing how the world understands the environmental footprint of food.
Now a Research Professor at Bard College and a Visiting Scholar at Harvard’s Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, he has become one of the most influential voices connecting daily dietary choices with global ecological outcomes.
With work in geophysics, agriculture and nutrition, Eshel offers a rare, systems-level view of how what we eat shapes the planet. His research has demonstrated, with striking clarity, that food is not merely a personal or cultural matter, but a driver of land use, water demand, and greenhouse gas emissions on a scale that challenges transportation and energy systems.
Your Grass-fed Burger isn’t Better for the Planet
For years, ranchers and some conservationists have argued that grass-fed beef is better for the planet than conventional cattle.
But a study published [March 2025] in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences challenges that idea, finding that cattle raised only on pastures do not have a smaller carbon footprint than feedlot cattle, which are quickly fattened on corn and other grains. This held even when the researchers took into account that healthy pastureland can help capture more carbon by pulling it out of the air and storing it in roots and other plant tissues.
How Your Plate Affects Your Planet
Humanity’s growing demand for animal meat is driving a planetary crisis, accelerating climate change, devastating ecosystems, and threatening public health.
Two grim, almost surreal, 26-story buildings tower over the southern outskirts of Enzhou, about 500 miles west of Shanghai in China’s Hubei province. No one would mistake them for apartment complexes despite their neat grid of window-like slots. Indeed, their main inhabitants are not human at all. The buildings are designed specifically to meet the biological and reproductive needs of 600,000 pigs each. Here they will be bred, farrowed, fattened, and finally slaughtered to meet the exploding animal protein needs of China, which consumes half the world’s pork and is also its biggest pork producer.
It is the world’s largest vertical pig farm, designed to manufacture 54,000 tonnes of pork every year. The building’s design reflects its unique function. Each of its six giant elevators can hoist a load of 10 tons, or about 100 pigs, at a time. Every utility and process, from the building’s water supply, electricity, and air conditioning, to its automatic feeding machines and smart air filtration and disinfection systems, can be monitored and controlled centrally from a NASA-like command center on the first floor. A stupendous amount of pig manure is processed daily in a biogas-driven waste treatment system and turned into electricity for lighting and heating the buildings. About 400 such ‘pig-rises’ could meet a part of China’s and the world’s growing appetite for animal proteins.
7 Steps to a More Sustainable Diet
Here are seven steps to a more sustainable diet.
Did you know that food production contributes about 21-37% of human-caused emissions?
To reduce your climate impact, eat more plant-based foods and reducing meat and dairy consumption, as these require fewer resources and produce fewer greenhouse gases.
Dr. Justina Ray: Listening to the Land
Dr. Justina Ray is not only protecting Canada’s wild spaces – she is about redefining how conservation itself is done. As President and Senior Scientist of Wildlife Conservation Society Canada, she has built a career that reaches far beyond field biology, asking what it truly means to sustain life across landscapes that shape both ecology and identity.
Her work has taken her to the tropical forests of Asia and Africa, the vast boreal and sub-arctic zones of Canada, and many places in-between guided by a singular conviction: science must serve the future of the living world.
Ray’s path into northern conservation began with questions rather than assumptions. How do wolverines and caribou survive when their ranges fragment? What happens when the climate itself becomes a moving target?
Our Broken Planet: How to heal our rainforests
Breathe in. Breathe out. The oxygen flowing through your body is the result of photosynthesis: the natural process through which living things convert sunlight into energy. About 30% of land-based photosynthesis happens in tropical rainforests. Rainforests are also great at sucking up excess carbon from the atmosphere – something we know we’ve got to do more of.
But in recent years, rainforests have been getting constricted: shrinking in size and choked up with smoke.
Listen to this podcast from the National History Museum to find out what’s going on and how we can help rainforests breathe deeply again.
Dr. Gosia Domagalska: Outwitting Leishmania
In the quiet corridors of the Institute of Tropical Medicine (ITM) in Antwerp, Belgium, Dr. Malgorzata “Gosia” Domagalska is leading the fight against one of the world’s most neglected yet devastating diseases: leishmaniasis. As head of ITM’s newly established Unit of Experimental Parasitology, she has dedicated her career to understanding how parasites adapt, survive, and outwit medicine.
Domagalska’s path to parasitology was anything but straightforward. Trained as a geneticist, she earned her PhD in Plant Genetics at the Max Planck Institute in Cologne, followed by a Marie Curie Fellowship at the University of York. Early on, her research focused on plant development and hormones. But a shift came when she joined ITM in 2015: “This work is compelling not just scientifically, but socially,” she has said.
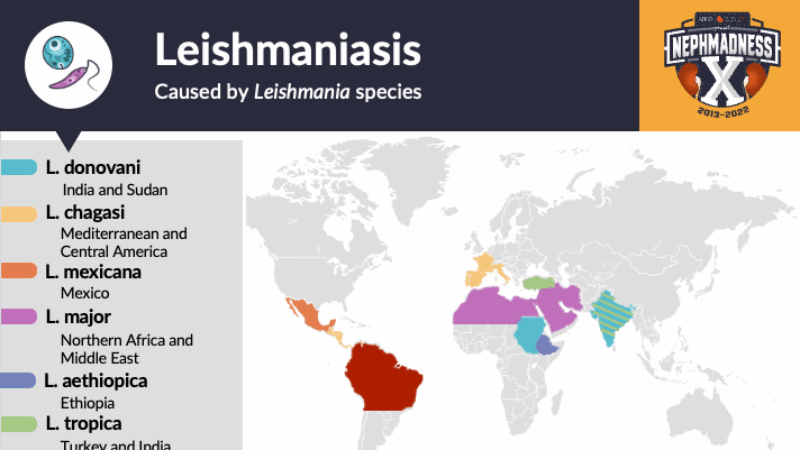
Epidemiology of Leishmaniasis
Leishmaniasis is a parasitic disease spread by the bite of infected female sandflies. It can affect the skin, mucous membranes, or internal organs. The most serious form, visceral leishmaniasis (VL), damages the liver, spleen, bone marrow, and kidneys, and is caused mainly by Leishmania donovani and Leishmania infantum.
Every year, 1–2 million people are affected, with over 90% of cases concentrated in just 13 countries. While many infections show no symptoms, untreated VL is usually fatal. Malnutrition, HIV co-infection, genetics, and young age (especially under 5) increase the risk of severe disease.
Dr. Regina Barzilay: From Patient to Pioneer
Dr. Regina Barzilay, a professor at MIT and a pioneer in artificial intelligence (AI), is not only moving the needle in science and technology – she is rebuilding the compass. Her work not only advances medical technology but also challenges how we think about diagnosis, treatment, and the human experience behind each.
Barzilay’s journey into medical AI did not begin in a lab. It began in a hospital room in 2014, when she received a breast cancer diagnosis. For most, that moment signals a personal battle. For her, it became something more. It became the beginning of a mission to reimagine cancer care through machine learning.
Six Ways AI is Transforming Healthcare
With 4.5 billion people currently without access to essential healthcare services and a health worker shortage of 11 million expected by 2030, AI has the potential to help bridge that gap and revolutionize global healthcare.
It could even get us back on track to meet the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal of achieving universal health coverage by 2030.
But while the technology is rapidly developing, healthcare is “below average” in its adoption of AI compared to other industries, according to the World Economic Forum’s white paper, The Future of AI-Enabled Health: Leading the Way.