Culture
Malik Afegbua: Storytelling at the Speed of Code
Malik Afegbua, born in Nigeria, considers himself a filmmaker, a visual artist, and a creative technologist. Afegbua is globally recognized for his ground-breaking use of artificial intelligence in storytelling.
A business-school graduate from the University of Surrey, he turned his focus to the creative realm in 2011 after receiving a Canon camera. This gift was the beginning of his career in photography, filmmaking and virtual storytelling. Today, he is the CEO of Slickcity Media, a Lagos‑based studio producing commercials, documentaries, VR experiences, and AI‑driven art for clients like Meta, Marvel Studios, IBM, American Express, and Cadbury.
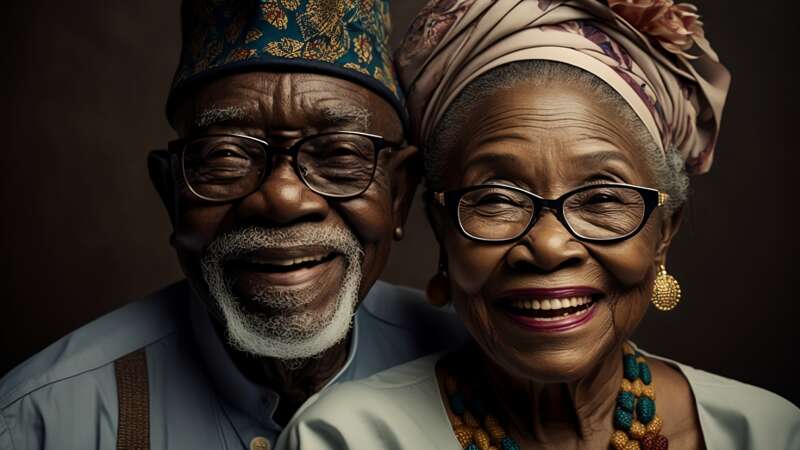
His breakout project, The Elder Series, also known as “Fashion Show for Seniors”, emerged in early 2023 when he used technology to depict elegantly dressed older adults walking a runway – imagining aging as stylish, powerful, and full of color. This collection went viral worldwide, earning praise from the World Health Organization during its Decade of Healthy Aging initiative.
Dr. Regina Barzilay: From Patient to Pioneer
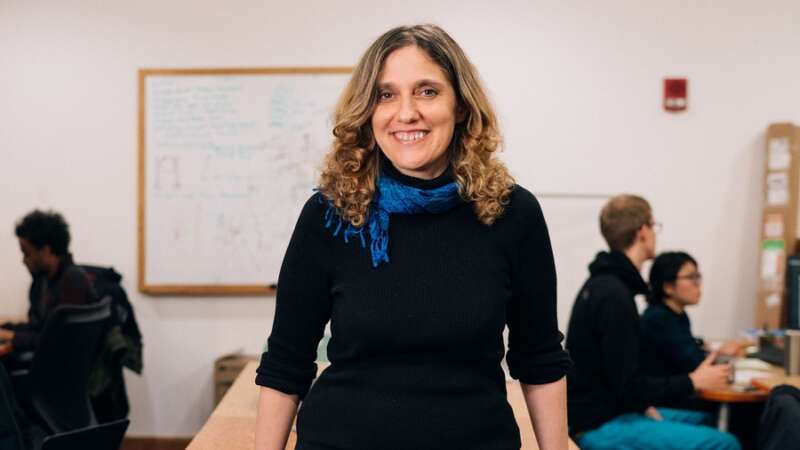
Dr. Regina Barzilay, a professor at MIT and a pioneer in artificial intelligence (AI), is not only moving the needle in science and technology – she is rebuilding the compass. Her work not only advances medical technology but also challenges how we think about diagnosis, treatment, and the human experience behind each.
Barzilay’s journey into medical AI did not begin in a lab. It began in a hospital room in 2014, when she received a breast cancer diagnosis. For most, that moment signals a personal battle. For her, it became something more. It became the beginning of a mission to reimagine cancer care through machine learning.
Six Ways AI is Transforming Healthcare
With 4.5 billion people currently without access to essential healthcare services and a health worker shortage of 11 million expected by 2030, AI has the potential to help bridge that gap and revolutionize global healthcare.
It could even get us back on track to meet the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal of achieving universal health coverage by 2030.
But while the technology is rapidly developing, healthcare is “below average” in its adoption of AI compared to other industries, according to the World Economic Forum’s white paper, The Future of AI-Enabled Health: Leading the Way.
AI in Telehealth: The New Game Changers
AI transforms health-seeking from an ordeal to a convenience for a busy city-dweller and a boon for those with mobility issues or living in remote areas. A few taps of a finger can schedule a consultation, and visiting a physician becomes as effortless as sitting before a TV. Around 75% of healthcare organizations have found that integrating AI into their operations improved their ability to treat diseases effectively while reducing staff burnout.
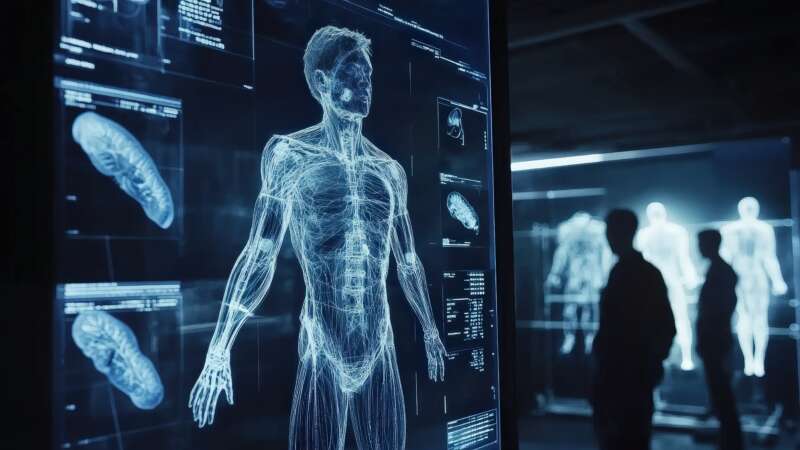
Since physical examinations contribute to only 11% of the diagnostic process, with the patient’s history making up 76%, AI has become a valuable tool for helping medical professionals assess and interpret patient data more efficiently. AI algorithms can rapidly process large datasets, allowing medical professionals to identify potential health risks early – often before they are detectable by traditional methods.
Telehealth and telemedicine is a booming market, projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 23.2% between 2023 and 2028 as technology advances, regulations evolve, and patients and healthcare professionals accept telemedicine as a safe, economical and viable choice. AI is dramatically re-drawing the telehealth landscape in the areas of prediction, diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of diseases like heart disease, cancer, respiratory disorders and diabetes, which account for nearly 75% of deaths worldwide each year.
Health care technology trends 2025
What is the future of AI in health care? What is the future of RPM? Is telehealth increasing or decreasing? How can AI reduce physician burnout?
This video from the American Medical Association, featuring a discussion between Margaret Lozovatsky, MD, vice president of Digital Health Innovations, and Todd Unger, CXO, answers all of these questions.
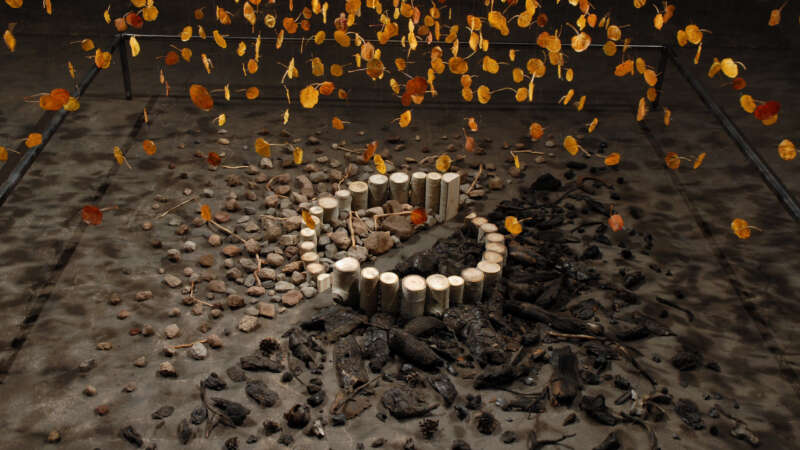
Bryan David Griffith: Art Born from Fire, Fueled by Purpose
Bryan David Griffith tackles big questions with simple materials. His art examines the tension between nature and culture, chaos and control, and life and loss. His engineering background brings a problem-solver’s mindset to his creative process, often inventing new techniques to serve each concept.
Griffith didn’t take a typical path into the art world. While studying at the University of Michigan, he found a beat-up photo manual, built a darkroom, and started experimenting. Later, disillusioned with a consulting job and its environmental impact, he quit, bought a van, and hit the road to become an artist.
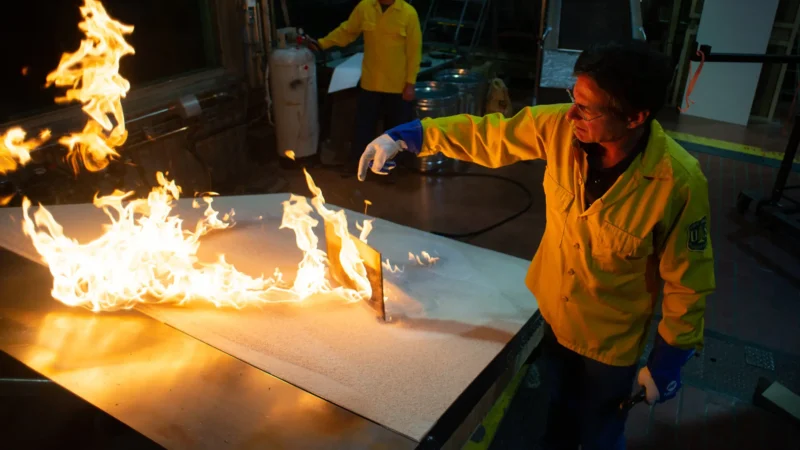
Dr. Mark Finney: Changing How We Fight (and live with) Fire
Dr. Mark Finney is a Senior Scientist and Research Forester with the U.S. Forest Service at the Missoula Fire Sciences Laboratory. With a Ph.D. in wildland fire science from UC Berkeley, Finney has spent decades exploring fire as both an ecological force and a physical process. His work has laid the foundation for many of the wildfire behavior models used today across the country.
Finney is a strong advocate for rethinking traditional fire suppression strategies. He emphasizes the need to let “good fire” play its role in the landscape, using tools like prescribed burns and targeted fuel treatments to prevent more extreme fires down the line. His research has revealed that long-held beliefs about how fires spread, such as the role of radiant heat, are often incorrect.
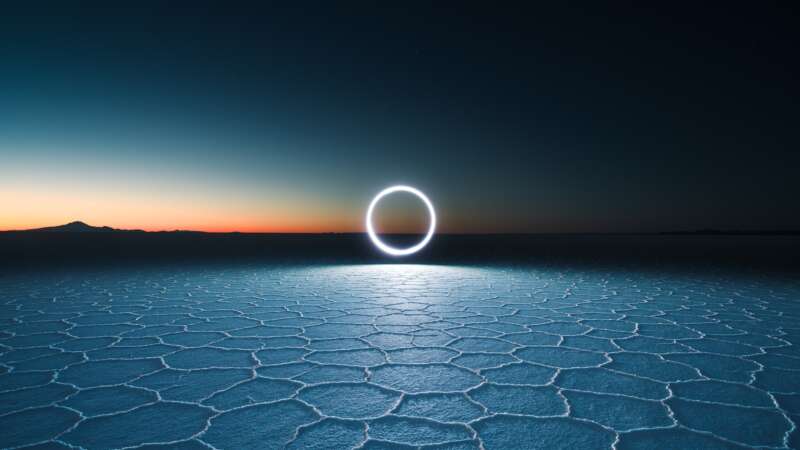
Reuben Wu: Shedding New Light on the World
Reuben Wu, a multidisciplinary artist who utilizes aerial lighting with drones and long-exposure photography, to tell compelling stories about the world we inhabit.
Wu has helped redefine contemporary landscape photography, and his work is featured in the permanent collections of the Guggenheim Museum, The Metropolitan Museum of Art, and the MoMA.
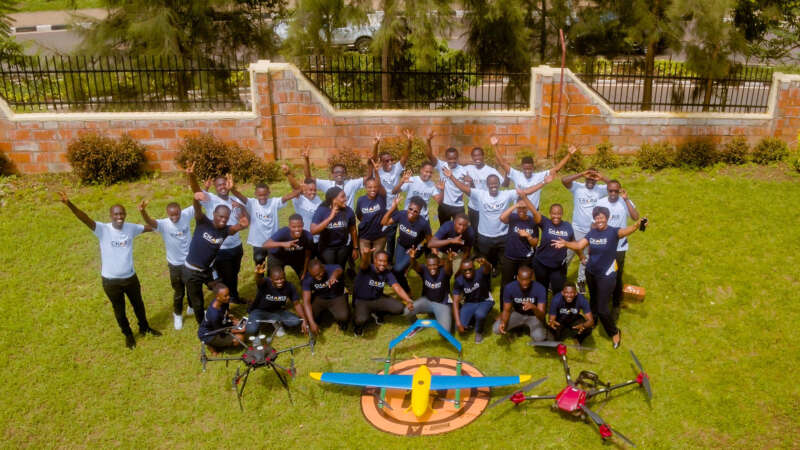
Mamy Ingabire: Transforming Vector Control in Africa
Mamy Ingabire is an entrepreneur dedicated to using cutting-edge technology to address critical challenges across various industries.
As the Managing Director of Charis UAS, Rwanda’s first licensed drone company, she has played a fundamental role in advancing the use of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) to improve efficiency in vector control, agriculture, construction, mapping, healthcare, and more. Under her leadership, Charis UAS has leveraged drone technology to revolutionize data collection and digital solutions.
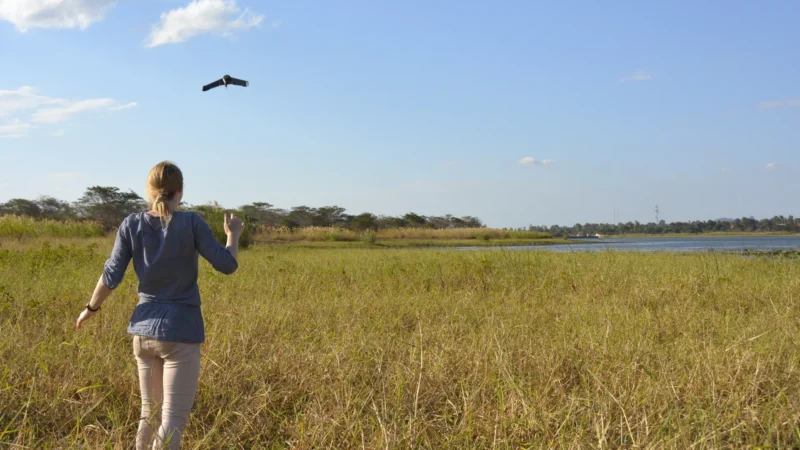
Drones vs. Mosquitoes: Fighting malaria in Malawi
In the middle of a muddy field next to a reservoir in north-western Malawi, a team of scientists are hard at work. Boxes of equipment lie scattered around a patch of dry ground, where a scientist programmes an automated drone flight into a laptop perched on a metal box. The craggy peak of Linga Mountain (‘watch from afar’ in the local language) looms over the lake, casting its reflection in the water.
With a high-pitched whirr of rotor blades, the drone takes off and starts following the shoreline, taking photos as it goes. Once the drone is airborne, the team switch from high-tech to low-tech mode. They collect ladles, rulers and plastic containers and squelch through mud until they reach the water’s edge.