Deficiency
How Your Plate Affects Your Planet
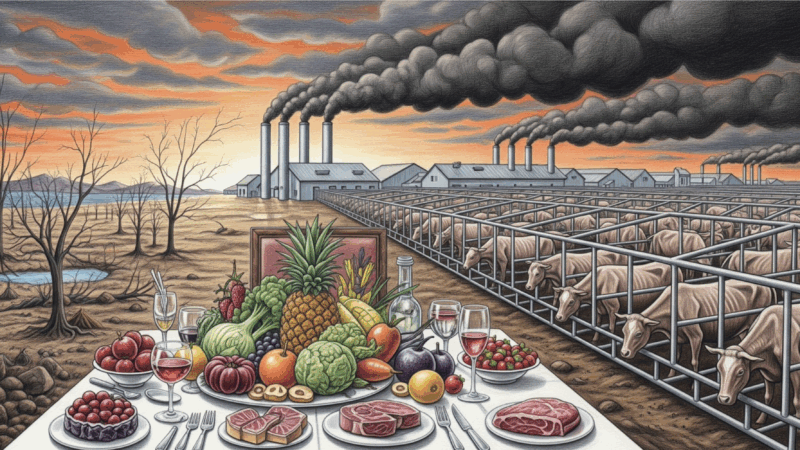
Humanity’s growing demand for animal meat is driving a planetary crisis, accelerating climate change, devastating ecosystems, and threatening public health.
Two grim, almost surreal, 26-story buildings tower over the southern outskirts of Enzhou, about 500 miles west of Shanghai in China’s Hubei province. No one would mistake them for apartment complexes despite their neat grid of window-like slots. Indeed, their main inhabitants are not human at all. The buildings are designed specifically to meet the biological and reproductive needs of 600,000 pigs each. Here they will be bred, farrowed, fattened, and finally slaughtered to meet the exploding animal protein needs of China, which consumes half the world’s pork and is also its biggest pork producer.
It is the world’s largest vertical pig farm, designed to manufacture 54,000 tonnes of pork every year. The building’s design reflects its unique function. Each of its six giant elevators can hoist a load of 10 tons, or about 100 pigs, at a time. Every utility and process, from the building’s water supply, electricity, and air conditioning, to its automatic feeding machines and smart air filtration and disinfection systems, can be monitored and controlled centrally from a NASA-like command center on the first floor. A stupendous amount of pig manure is processed daily in a biogas-driven waste treatment system and turned into electricity for lighting and heating the buildings. About 400 such ‘pig-rises’ could meet a part of China’s and the world’s growing appetite for animal proteins.
Role of Social Determinants in Maternal and Child Health
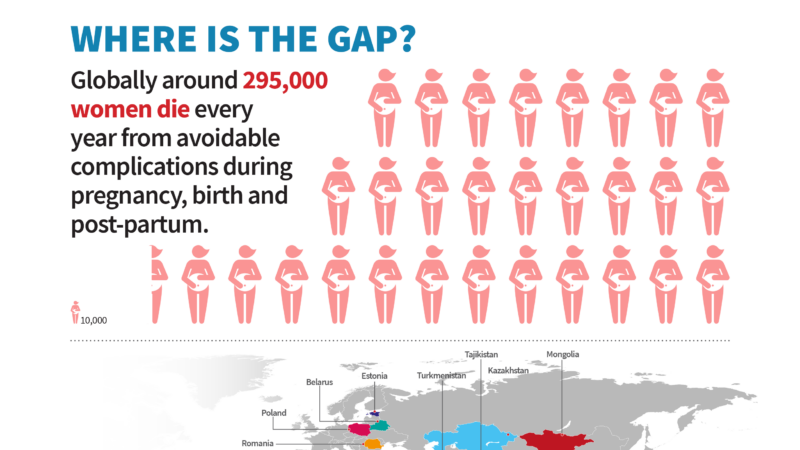
About 287,000 women died during and following pregnancy and childbirth in 2020. Around 95% of these maternal deaths occurred in low and lower middle-income countries and nearly every death was preventable. Equally, children under the age of five continue to face differing chances of survival based on where they are born and raised.
A child born in sub-Saharan Africa is 11 times more likely to die in the first month of life than one born in the region of Australia and New Zealand, and a 15-year-old girl in sub-Saharan Africa is 400 times more likely to die in her lifetime due to issues related to childbirth than a 15-year-old girl living in Australia and New Zealand (with the ratio for SSA being 1 in 40, compared to ANZ being 1 in 16,000 women).
Where is the Maternal Health Gap?
Maternal health has long been a central focus in global initiatives, prominently featured in key frameworks such as the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs), the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), and the Global Strategy for Women’s, Children’s, and Adolescents’ Health.
Unfortunately, despite these efforts, the ambitious targets—particularly those aimed at reducing maternal mortality—remain unmet.
A recent report from the Copenhagen Consensus Center highlights these challenges, and this infographic offers further insight into the statistics.
Gary White: Making Waves in the Fight for Clean Water
Gary White, Co-founder and CEO of Water.org and WaterEquity, is a visionary leader dedicated to addressing the worldwide water crisis. His commitment originated from observing the severe conditions experienced by communities in Honduras lacking safe water and sanitation facilities.
Committed to effecting change, he arranged a fundraising dinner that generated sufficient resources to provide water to a village. This act served as inspiration for establishing WaterPartners International, presently recognized as Water.org, an organization that has significantly improved the well-being of millions of individuals worldwide.
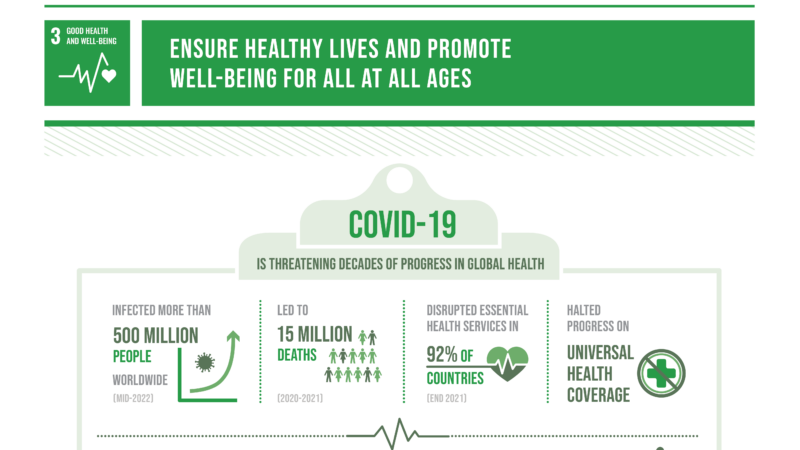
Breaking Down UN SDG 3: Good Health and Well-Being
The United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3) aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all. From reducing maternal and child mortality to combating infectious diseases, SDG 3 encompasses a wide range of health-related issues that are essential for building a sustainable planet.
In this infographic, we will delve deeper into the specific targets of SDG 3 and examine the progress made so far in achieving them. Join us as we explore the importance of good health and well-being, and the steps we can take to make it a reality for everyone.
Earth Day & Public Health: Unavoidably Connected
Each year on April 22nd, people and nations around the world celebrate Earth Day to raise awareness and promote action toward environmental protection and sustainability. Activities typically include community clean-ups and educational campaigns designed to promote sustainability in daily life.
The origins of Earth Day date back to the 1960s and a decade of growing enviro-consciousness brought about by the publication of Rachel Carson’s Silent Spring and a series of environmental disasters that climaxed with a devastating oil spill off the coast of California in 1969. Gaylord Nelson, a U.S. Senator from Wisconsin, organized the first Earth Day in 1970, when an estimated 20 million Americans took part in organized activities ranging from tree plantings to beach cleanups and teach-ins on college campuses.
Since those humble beginnings, Earth Day has become a global event – but amidst the tree plantings and landscape revitalization lies a subtle and yet direct connection between Earth Day and Public Health. Just as we depend on the natural environment for our survival, civilization creates and shapes a social and economic environment that greatly influences the health and well-being of our species.
Eight Trends Shaping Global Healthcare
The challenges faced by the global health and healthcare sector are set to continue in the future. The near-term issues include worsening mental health, healthcare workforce shortages, supply chain issues, climate change-related challenges and macroeconomic instability. The longer-term challenges include growing demand for services, an increasing funding gap, a lack of incentives for innovation, widening disparities in overall health and wellness, and variable access to advanced therapies.
As we approach World Health Day on 7 April, here are eight current global health and healthcare trends we need to contend with as we aim to transform systems to become more sustainable, resilient and equitable.