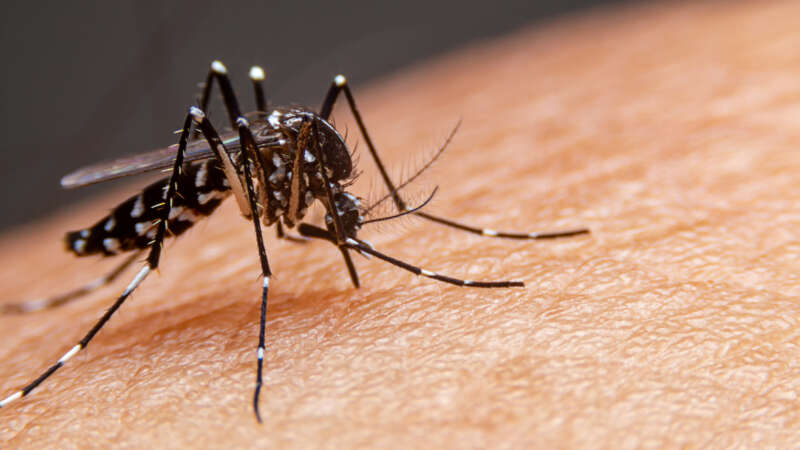
Aedes aegypti
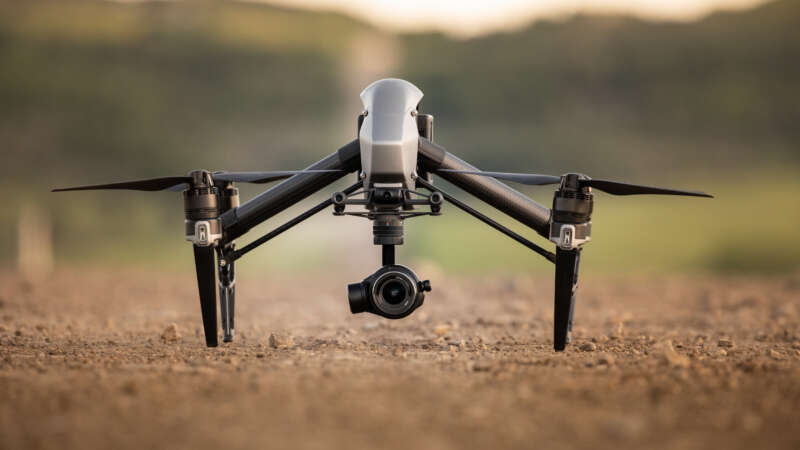
The Drone Edge in Vector Control
Achieving global vector control’s potential requires “realigning programs to optimize the delivery of interventions that are tailored to the local context [and]…strengthened monitoring systems and novel interventions with proven effectiveness.” This includes “integration of non-chemical and chemical vector control methods [and] evidence-based decision making guided by operational research and entomological and epidemiological surveillance and evaluation.”
Drones or “unmanned aerial vehicles” (UAVs) can save time and money compared to conventional ground-based surveys. Sophisticated models and monitoring equipment can be purchased for a few thousand dollars. They don’t require a pilot’s license, they are becoming easier to fly, and their paths can be fully automated through AI, machine learning, global positioning systems, and computer vision.
Shrinking Forests, Emerging Diseases
Dona Dora’s man is away from home a lot more these days. It didn’t used to be like that.
He leaves early, sometimes on foot, but increasingly on his bicycle, and heads into the forests surrounding Belém, the capital of Brazil’s Para province. He keeps his eyes open especially for five medicinal plants that are always in demand — sucuúba (Himatanthus sucuuba), copaíba (Copaifera spp.), andiroba (Carapa guianensis), barbatimão (Stryphnodendron spp.) and pãu d’arco (Tabebuia avellanedae).
Fifteen years earlier, he would have found all five within hours and been back for lunch, but times have changed. These days, medicinal forest plants in high demand are becoming harder to find as forests that have stood strong for millennia are cleared to make way for grazing pastures for millions of cattle, agriculture, and development.
Now, Dona Dora’s man can spend a whole day and not find more than a few plants. It might be late at night before he gets back home.
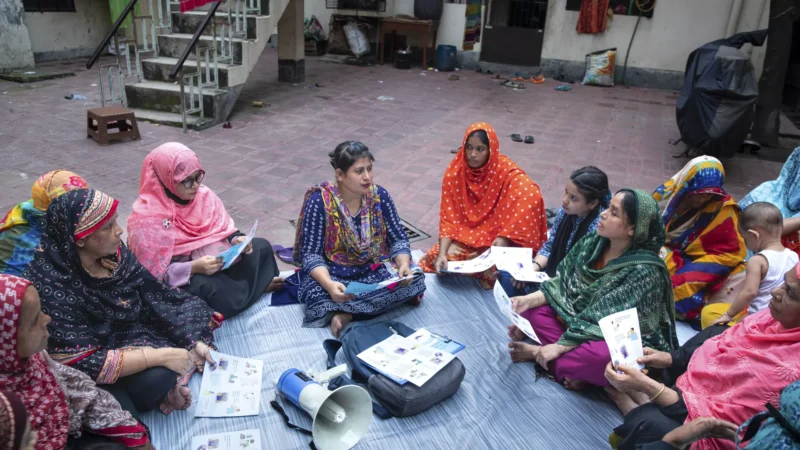
Shiuly Khatun: Dengue Warrior
Shiuly Khatun is a Field Supervisor at the Dhalpur Aalo Clinic in Dhaka, Bangladesh, where she manages and coordinates the clinic’s operations. Her daily responsibilities are vast and critical, ranging from mapping areas and dividing work for community volunteers to conducting health sessions and overseeing satellite clinic activities.
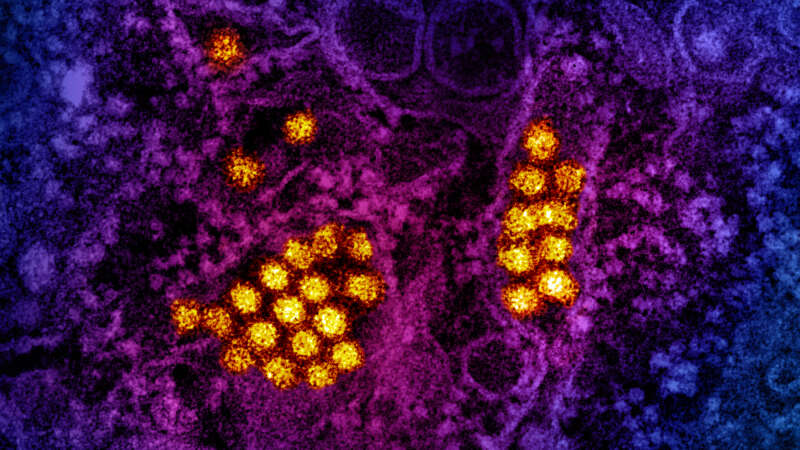
Dengue fever, once confined to the tropics, now threatens the U.S.
Climate change is expanding the habitat of the mosquitoes that carry the disease, allowing them to spread further north.
Meg Norris was traveling in Argentina in April when the first signs of dengue fever hit her. The weather in Salta, just south of the Bolivian border, was warm, but Norris, a 33-year-old from Boulder, Colorado, zipped a fleece sweatshirt around her body to stop herself from shivering.
“I thought it was sun poisoning,” she said.
Dengue Explained in Five Minutes
Check out this video by Free Med Education to learn about dengue fever, its cause, and its symptoms.
The Rise of Dengue: A Global Perspective
Around the world, dengue is considered the most common viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes that affects people. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the disease is now endemic in more than 100 countries. In the first three months of 2024, over five million dengue cases and over 2000 dengue-related deaths were reported globally. The figures so far project that 2024 could be even worse than 2023, with the regions most seriously affected being the Americas, South-East Asia, and Western Pacific.
In the Americas, there were 6,186,805 suspected cases of dengue reported in the first 15 weeks of 2024. To put this into perspective, according to the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), this figure represents an increase of 254% compared to the same period in 2023. Of these cases 5,928 were confirmed and classified as severe dengue.
The Economics of Resistance
It would be extremely difficult to calculate, with any high degree of accuracy, the global economic impact of insecticide resistance. For starters, we must consider that insect management plays a pivotal role in a variety of sectors – agriculture, home and garden, forestry, structural applications, and vector control. Analysis of the totality of economic impacts arising from resistance in any one of these sectors quickly becomes a complicated interplay of variables that interact within that given system.
To account for the full economic impact, one must layer in the amount being spent on insect management and how much of that investment is lost to resistance, but also the economic impact of losses to the overarching objectives of a given program.
To calculate the impact, you must first calculate what is at risk.
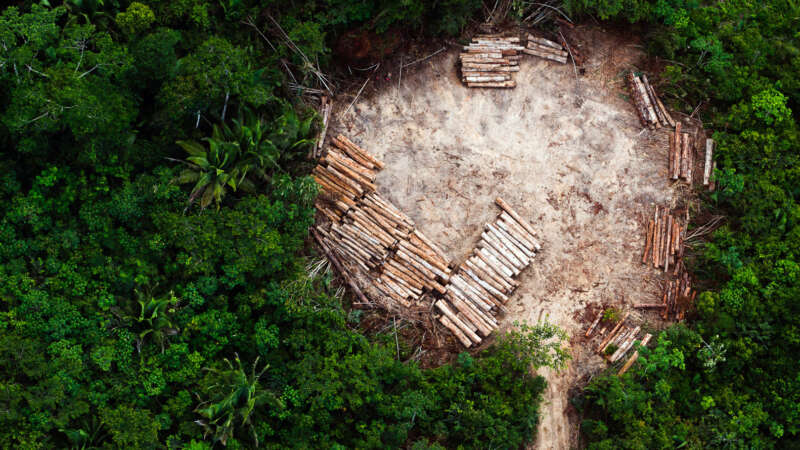
Deforestation’s Hidden Toll: Amplifying Disease Risk Worldwide
In the last couple of decades, the lush rainforest around the remote village of Meliandou in the heart of Guinea has become patchier. Animals, like bats, saw their habitats dwindle and in a quest for survival, they sought refuge in closer proximity to human environments, making the boundaries between species thinner. A hollowed-out tree in the middle of the village became home to a colony of bats.
About 50 meters from the same tree, in the heart of Meliandou, a two-year-old boy named Emile lived with his family. In a matter of days, Emile fell ill with an unknown virus, developed a high fever, and died. Soon the same virus, that scientists now believe Emile got from the bats, took the lives of his sister, mother, and grandmother. The village, surrounded by a ring of forest, unexpectedly became the epicenter of a devastating outbreak that would leave an indelible mark.
Dr. Raman Velayudhan: Combating Deadly Mosquitoes
Dr. Raman Velayudhan is a seasoned expert in the public health field and a relentless advocate for combating the global threat of mosquito-borne diseases.
Currently at the helm of the Veterinary Public Health, Vector Control, and Environment unit within the Department of Control of Neglected Tropical Diseases at the World Health Organization (WHO), Dr. Velayudhan’s impact is far-reaching.