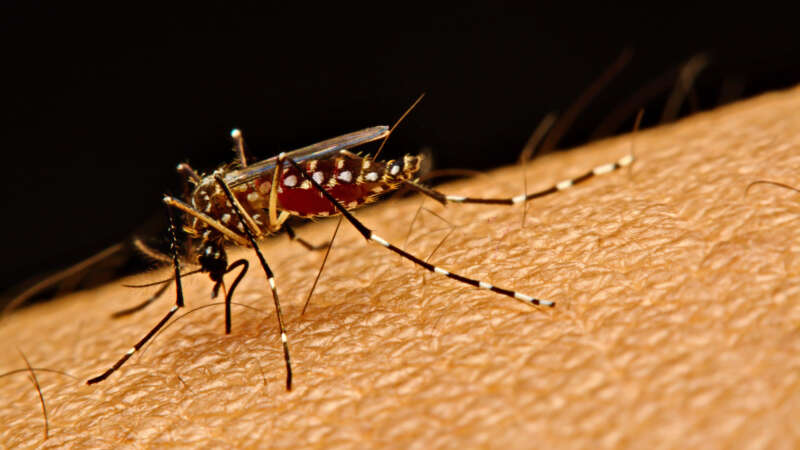
Aedes
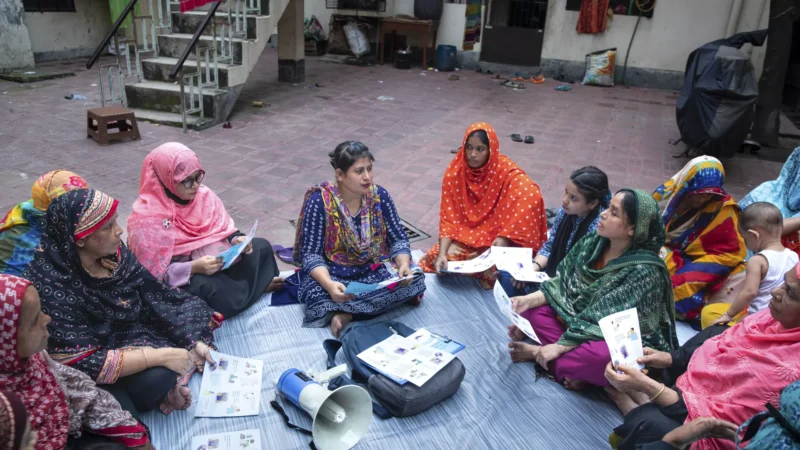
Shiuly Khatun: Dengue Warrior
Shiuly Khatun is a Field Supervisor at the Dhalpur Aalo Clinic in Dhaka, Bangladesh, where she manages and coordinates the clinic’s operations. Her daily responsibilities are vast and critical, ranging from mapping areas and dividing work for community volunteers to conducting health sessions and overseeing satellite clinic activities.
Dengue fever, once confined to the tropics, now threatens the U.S.
Climate change is expanding the habitat of the mosquitoes that carry the disease, allowing them to spread further north.
Meg Norris was traveling in Argentina in April when the first signs of dengue fever hit her. The weather in Salta, just south of the Bolivian border, was warm, but Norris, a 33-year-old from Boulder, Colorado, zipped a fleece sweatshirt around her body to stop herself from shivering.
“I thought it was sun poisoning,” she said.
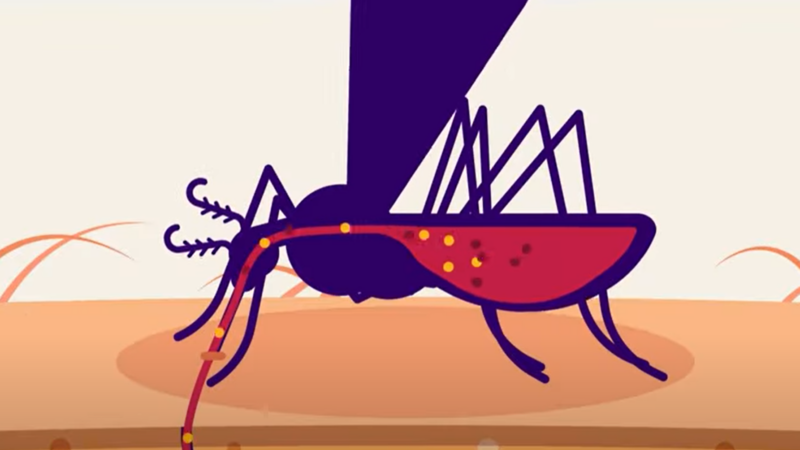
Dengue Explained in Five Minutes
Check out this video by Free Med Education to learn about dengue fever, its cause, and its symptoms.
The Rise of Dengue: A Global Perspective
Around the world, dengue is considered the most common viral disease transmitted by mosquitoes that affects people. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the disease is now endemic in more than 100 countries. In the first three months of 2024, over five million dengue cases and over 2000 dengue-related deaths were reported globally. The figures so far project that 2024 could be even worse than 2023, with the regions most seriously affected being the Americas, South-East Asia, and Western Pacific.
In the Americas, there were 6,186,805 suspected cases of dengue reported in the first 15 weeks of 2024. To put this into perspective, according to the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), this figure represents an increase of 254% compared to the same period in 2023. Of these cases 5,928 were confirmed and classified as severe dengue.
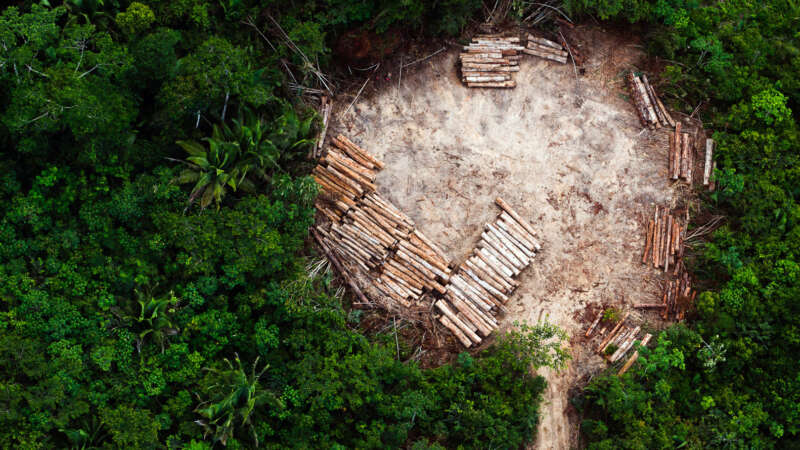
Deforestation’s Hidden Toll: Amplifying Disease Risk Worldwide
In the last couple of decades, the lush rainforest around the remote village of Meliandou in the heart of Guinea has become patchier. Animals, like bats, saw their habitats dwindle and in a quest for survival, they sought refuge in closer proximity to human environments, making the boundaries between species thinner. A hollowed-out tree in the middle of the village became home to a colony of bats.
About 50 meters from the same tree, in the heart of Meliandou, a two-year-old boy named Emile lived with his family. In a matter of days, Emile fell ill with an unknown virus, developed a high fever, and died. Soon the same virus, that scientists now believe Emile got from the bats, took the lives of his sister, mother, and grandmother. The village, surrounded by a ring of forest, unexpectedly became the epicenter of a devastating outbreak that would leave an indelible mark.
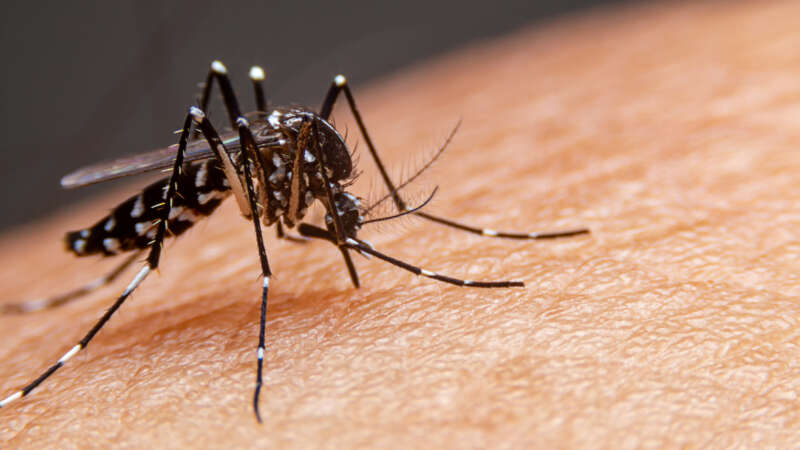
Aedes aegypti: Beyond the Black and White
One look at Aedes aegypti gives an immediate impression of its menacing nature. The telltale dark and white bands on the mosquito’s legs and other body parts bring a sense of foreboding and hardship. Sleek, silent, and stealthy, Ae. aegypti is the primary vector for several important, debilitating, and sometimes fatal human diseases including dengue, Zika virus, yellow fever, and chikungunya. The species is cause for mounting concern on many levels, as its biology, behavior, and ability to adapt have made Aedes aegypti one of the most pervasive and daunting public health challenges in the modern world.
The first mosquito ever associated with the spread of disease, Ae. aegypti is also the most studied of all mosquito species.1 From its humble beginnings in the African wild to a footprint that spans the globe, this durable and opportunistic insect has become a formidable opponent of vector control efforts worldwide.
What Happened with Zika
Five powerful positives that emerged in the wake of the 2016 Zika outbreakThink back two years to 2016. Never a day went by when there …
Long-Term Project Seeks To Build Guidelines for Area-Wide Asian Tiger Mosquito Control
A long-term project to determine the best methods of controlling Aedes albopictus, the Asian tiger mosquito, is in the third of at least five years …
Full-Scale Assault Now Under Way as Key West District Battles Dengue
Swarms of them come from near and far, creating a furor in Key West, Florida. “They” are not mosquitoes. They are representatives of the national …
Container Species Control in Mercer County
Area-wide larviciding using truck-mounted low-volume technology will be among the recommendations from a five-year, $3.8 million U.S. Department of Agriculture project to control the Asian …