AI
Malik Afegbua: Storytelling at the Speed of Code
Malik Afegbua, born in Nigeria, considers himself a filmmaker, a visual artist, and a creative technologist. Afegbua is globally recognized for his ground-breaking use of artificial intelligence in storytelling.
A business-school graduate from the University of Surrey, he turned his focus to the creative realm in 2011 after receiving a Canon camera. This gift was the beginning of his career in photography, filmmaking and virtual storytelling. Today, he is the CEO of Slickcity Media, a Lagos‑based studio producing commercials, documentaries, VR experiences, and AI‑driven art for clients like Meta, Marvel Studios, IBM, American Express, and Cadbury.
His breakout project, The Elder Series, also known as “Fashion Show for Seniors”, emerged in early 2023 when he used technology to depict elegantly dressed older adults walking a runway – imagining aging as stylish, powerful, and full of color. This collection went viral worldwide, earning praise from the World Health Organization during its Decade of Healthy Aging initiative.
Dr. Regina Barzilay: From Patient to Pioneer
Dr. Regina Barzilay, a professor at MIT and a pioneer in artificial intelligence (AI), is not only moving the needle in science and technology – she is rebuilding the compass. Her work not only advances medical technology but also challenges how we think about diagnosis, treatment, and the human experience behind each.
Barzilay’s journey into medical AI did not begin in a lab. It began in a hospital room in 2014, when she received a breast cancer diagnosis. For most, that moment signals a personal battle. For her, it became something more. It became the beginning of a mission to reimagine cancer care through machine learning.
Six Ways AI is Transforming Healthcare
With 4.5 billion people currently without access to essential healthcare services and a health worker shortage of 11 million expected by 2030, AI has the potential to help bridge that gap and revolutionize global healthcare.
It could even get us back on track to meet the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal of achieving universal health coverage by 2030.
But while the technology is rapidly developing, healthcare is “below average” in its adoption of AI compared to other industries, according to the World Economic Forum’s white paper, The Future of AI-Enabled Health: Leading the Way.
AI in Telehealth: The New Game Changers
AI transforms health-seeking from an ordeal to a convenience for a busy city-dweller and a boon for those with mobility issues or living in remote areas. A few taps of a finger can schedule a consultation, and visiting a physician becomes as effortless as sitting before a TV. Around 75% of healthcare organizations have found that integrating AI into their operations improved their ability to treat diseases effectively while reducing staff burnout.
Since physical examinations contribute to only 11% of the diagnostic process, with the patient’s history making up 76%, AI has become a valuable tool for helping medical professionals assess and interpret patient data more efficiently. AI algorithms can rapidly process large datasets, allowing medical professionals to identify potential health risks early – often before they are detectable by traditional methods.
Telehealth and telemedicine is a booming market, projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 23.2% between 2023 and 2028 as technology advances, regulations evolve, and patients and healthcare professionals accept telemedicine as a safe, economical and viable choice. AI is dramatically re-drawing the telehealth landscape in the areas of prediction, diagnosis, treatment and monitoring of diseases like heart disease, cancer, respiratory disorders and diabetes, which account for nearly 75% of deaths worldwide each year.
Health care technology trends 2025
What is the future of AI in health care? What is the future of RPM? Is telehealth increasing or decreasing? How can AI reduce physician burnout?
This video from the American Medical Association, featuring a discussion between Margaret Lozovatsky, MD, vice president of Digital Health Innovations, and Todd Unger, CXO, answers all of these questions.
Supercomputer Using AI to Develop Vaccines
A £225m supercomputer is using artificial intelligence (AI) to develop new drugs and vaccines.
When it is fully operational this summer, the Isambard-AI computer in Bristol will be the most powerful supercomputer in the UK.
Last week, Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer unveiled plans to “unleash AI” across the UK in an effort to boost growth.
Simon McIntosh-Smith, a professor in high-performance computing at Bristol University, said the Isambard-AI meant the UK “genuinely can be competitive with the world”.
Purdue launches new AI-based global forest mapping project
Purdue University’s Jingjing Liang has received a two-year, $870,000 grant from the World Resources Institute to map global forest carbon accumulation rates.
“To accurately capture the carbon accumulation rates of forested ecosystems across the world has always been a challenging task, mostly because doing so requires lots of ground-sourced data, and currently such data are very limited to the scientific community,” said Liang, an associate professor of quantitative forest ecology and co-director of the Forest Advanced Computing and Artificial Intelligence Lab.
“This task is considerably more challenging than mapping carbon emissions from forest loss,” said Nancy Harris, research director of the Land & Carbon Lab at the World Resources Institute, a nonprofit research organization based in Washington, D.C. “With emissions, there’s a clear signal in satellite imagery when trees are cut, leading to a big drop in forest carbon stocks and a relatively abrupt pulse of emissions to the atmosphere. With sequestration, forests accumulate carbon gradually and nonlinearly.”
The Role of Technology in Forest Management
In Brazil’s Pará region, new roads are cutting through the pristine Amazon rainforest, opening up once-untouched areas to human activities. Expansive stretches of lush greenery are vanishing at an alarming pace, yielding to barren patches and freshly cleared land.
Meanwhile, far into space, the European Space Agency captures high-resolution satellite images of the region that unveil an important pattern: deforestation occurs predominantly near these newly constructed roads.
Back in 2016, it sparked a question: what if there were a tool to monitor these roads and forecast potential deforestation areas? Not long after PrevisIA was born.
In 2021, Microsoft with Vale Fund and the Amazon Institute for Man and the Environment (Imazon) developed a new AI tool called PrevisIA, to predict deforestation hotspots in the Amazon. Using satellite imagery from the European Space Agency and an algorithm developed by Imazon, the tool produces heat maps showing the most exposed conservation areas, Indigenous lands, and other settlements, along with rankings for states and municipalities.
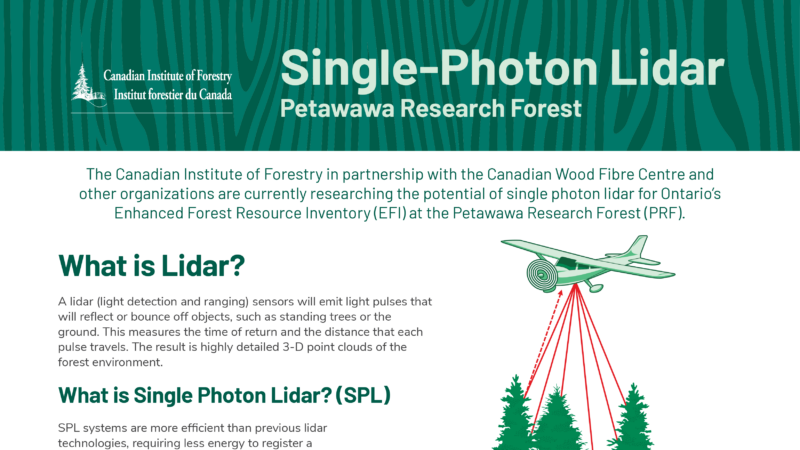
Single-Photon Lidar
The Canadian Institute of Forestry in partnership with the Canadian Wood Fibre Centre and other organizations are currently researching the potential of single photon lidar for Ontario’s
Enhanced Forest Resource Inventory (EFI) at the Petawawa Research Forest (PRF).
What is Lidar?
A lidar (light detection and ranging) sensors will emit light pulses that will reflect or bounce off objects, such as standing trees or the ground. This measures the time of return and the distance that each pulse travels. The result is highly detailed 3-D point clouds of the forest environment.
Anna Dumitriu: Exploring the Intersection of Art, Science, & Technology
British artist Anna Dumitriu’s name is synonymous with the world of BioArt. Not only is her work visually stunning, but it is also intellectually stimulating, as she tackles some of the most pressing issues of our time.
Dumitriu’s art explores our relationship to infectious diseases, artificial intelligence, and the impact of the pandemic from cultural and scientific perspectives. During her exploration of these topics, she has worked with the Liu Laboratory for Synthetic Evolution at the University of California in Irvine to investigate synthetic biology, and she has collaborated with BeyondSequ at the University of Birmingham to visually observe her CRISPR edit using super-resolution laser microscopy.