carbon sequestration
Indigenous Peoples’ Role in Protecting Forest Health
Nearly a quarter of the world’s population, or about 1.6 billion people, depend on forest resources to sustain their livelihood. This number includes an estimated 60 million who are members of indigenous groups. The worldviews of most indigenous cultures include a sacred obligation to serve as stewards of a healthy forest that can sustain its inhabitants for generations.
Indigenous peoples have been effectively managing their forests since “time immemorial,” yet governmental and scientific forestry experts have only recently begun to seek out the knowledge that indigenous peoples have about environmental management.
Stephen Nicholson: A Life Dedicated to Forest Health
Stephen Nicholson’s career in forest health and protection spans almost five decades, during which he has dedicated himself to developing and improving methods for applying pesticides and training others in their use. Today, we have the privilege of discussing his expertise and accomplishments in forest health and protection.
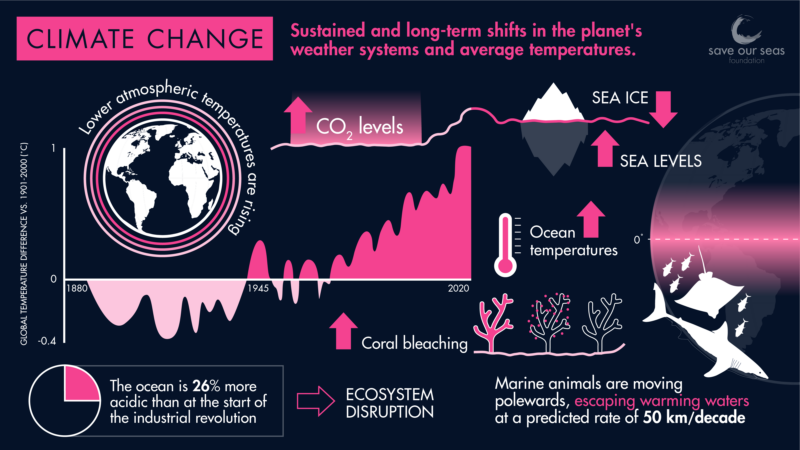
Infographic: Carbon & The Sea
By releasing greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, humans are changing the global climate in ways that are affecting the marine environment in terms of weather patterns, water temperature, sea level, ocean chemistry, currents, coastal erosion and the frequency of storms.
Forests & Earth’s Temperatures
Seeing the forest through the trees is an expression you may not think of when the topic of global warming comes up. However, 31% of the earth’s surface is covered by trees and each one is working overtime to sequester carbon to combat global warming. Carbon sequestration is a natural or artificial process by which carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere and held in solid or liquid form, and it is estimated that forests absorb approximately 7.6 billion metric tons of carbon annually.
Health Impacts of Climate Change
The debate about whether climate change is a real phenomenon – and whether humankind is responsible for the alarming rise in greenhouse gas (GHG) levels – is largely a thing of the past. Three decades of research has put forth what most scientists consider incontrovertible proof that escalating levels of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O) are a direct result of human activities ranging from deforestation to emissions from energy production, industry, and agriculture.