climate change
Justin Brice Guariglia: A Visual Provocateur
tin Brice Guariglia moves fluidly between art, science, and activism, all the while creating work that pushes its viewers to face the realities of a rapidly shifting planet. His practice grows out of collaborations with scientists, writers, and thinkers.
Guariglia’s perspective was transformed in 2015, when he joined NASA missions over Greenland to document its melting ice sheets. Seeing the scale of change firsthand reshaped his artistic direction and led to deeper partnerships with climate researchers. These experiences have since fed into everything from large-scale public installations to digital projects exploring sea-level rise. His ongoing work with research institutions and climate-focused organizations shows his genuine commitment to bridging scientific knowledge and public understanding.
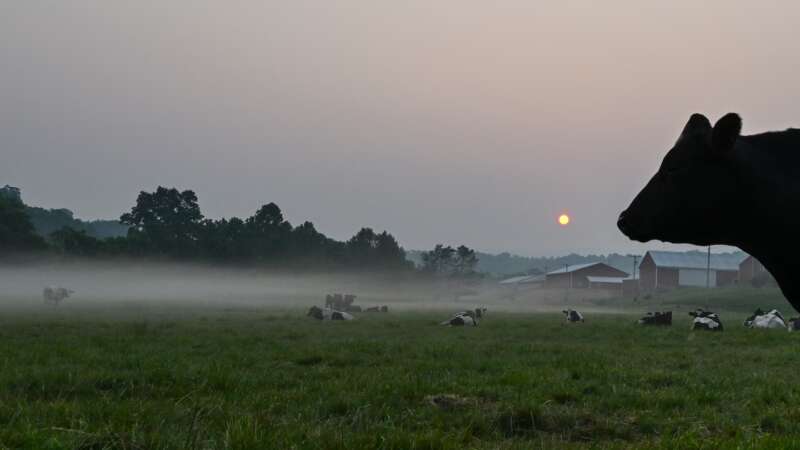
Your Grass-fed Burger isn’t Better for the Planet
For years, ranchers and some conservationists have argued that grass-fed beef is better for the planet than conventional cattle.
But a study published [March 2025] in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences challenges that idea, finding that cattle raised only on pastures do not have a smaller carbon footprint than feedlot cattle, which are quickly fattened on corn and other grains. This held even when the researchers took into account that healthy pastureland can help capture more carbon by pulling it out of the air and storing it in roots and other plant tissues.
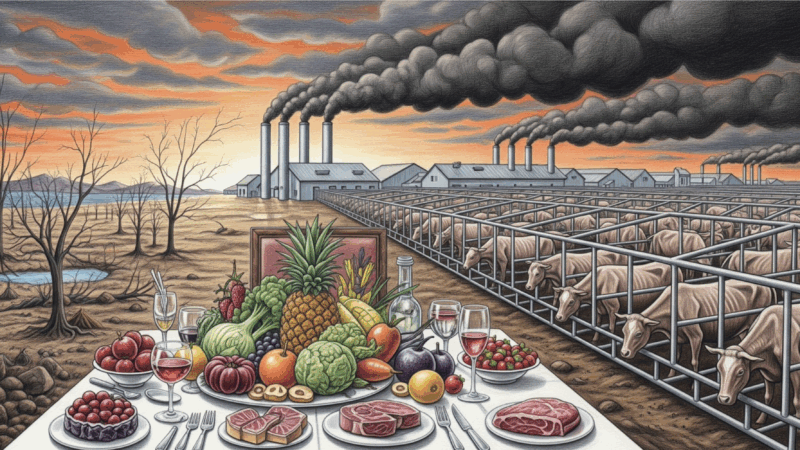
How Your Plate Affects Your Planet
Humanity’s growing demand for animal meat is driving a planetary crisis, accelerating climate change, devastating ecosystems, and threatening public health.
Two grim, almost surreal, 26-story buildings tower over the southern outskirts of Enzhou, about 500 miles west of Shanghai in China’s Hubei province. No one would mistake them for apartment complexes despite their neat grid of window-like slots. Indeed, their main inhabitants are not human at all. The buildings are designed specifically to meet the biological and reproductive needs of 600,000 pigs each. Here they will be bred, farrowed, fattened, and finally slaughtered to meet the exploding animal protein needs of China, which consumes half the world’s pork and is also its biggest pork producer.
It is the world’s largest vertical pig farm, designed to manufacture 54,000 tonnes of pork every year. The building’s design reflects its unique function. Each of its six giant elevators can hoist a load of 10 tons, or about 100 pigs, at a time. Every utility and process, from the building’s water supply, electricity, and air conditioning, to its automatic feeding machines and smart air filtration and disinfection systems, can be monitored and controlled centrally from a NASA-like command center on the first floor. A stupendous amount of pig manure is processed daily in a biogas-driven waste treatment system and turned into electricity for lighting and heating the buildings. About 400 such ‘pig-rises’ could meet a part of China’s and the world’s growing appetite for animal proteins.
7 Steps to a More Sustainable Diet
Here are seven steps to a more sustainable diet.
Did you know that food production contributes about 21-37% of human-caused emissions?
To reduce your climate impact, eat more plant-based foods and reducing meat and dairy consumption, as these require fewer resources and produce fewer greenhouse gases.
Protecting Earth’s Lungs
Forests act as the planet’s terrestrial lungs. They provide us with fresh air, clean water, beautiful vistas and a sanctuary for countless wildlife.
But, today, more than ever, our forests are facing unprecedented threats from disease, climate change, mad-made destruction and harmful pests.
Join this documentary as it follows a group of professionals that developed, tested and formulated today’s forest health strategies to preserve the legacy of one of the planet’s most important resources – and to help us better understand and appreciate why we need to protect our forests.
This is a story that affects us all.
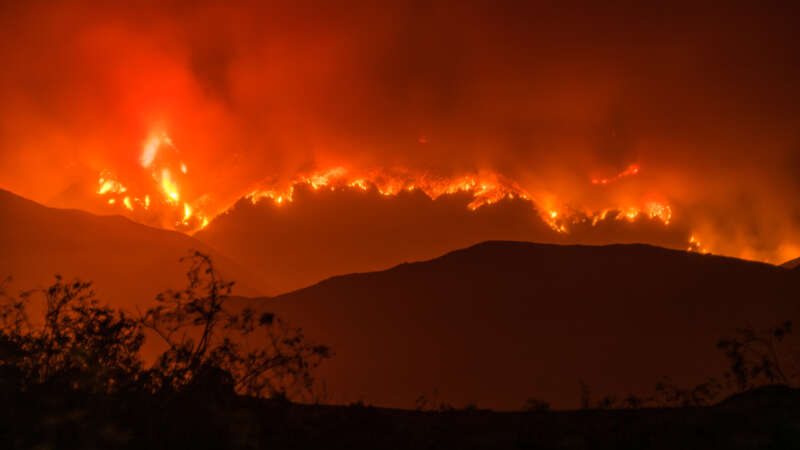
The Age of Firestorms
Dr. Roslyn Prinsley never imagined that stepping outside her home in Canberra would feel like walking into a smoke-filled abyss. But during Australia’s devastating bushfire season in 2019-2020, even in places untouched by flames, the air was so thick with smoke that breathing felt impossible.
“I asked myself, what are we doing here in the 21st century? We can’t actually go outside and breathe fresh air in one of the cleanest countries in the world,” she remembers thinking. “We can’t let this keep going.”
Dr. Roslyn Prinsley is the Head of Disaster Solutions at the Australian National University’s Institute for Climate, Energy & Disaster Solutions (ICEDS). Finding innovative ways to fight wildfires is part of her daily work – a task that has become more urgent than ever as wildfires grow increasingly frequent in Australia and across the globe due to climate change.
Wildfires are projected to rise 30% by the end of 2050, according to a report by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) and its partner GRID-Arendal.
One of the recent wildfires in California became the most destructive in Los Angeles history, killing at least 29 people—a number expected to rise—and reducing over 10,000 homes to ash. A perfect set of environmental factors such as long-term drought, preceding heavy rainfall, and hurricane-force Santa Ana winds combined at the worst possible moment.
All of this turned the regular wildfire into what’s called a firestorm.
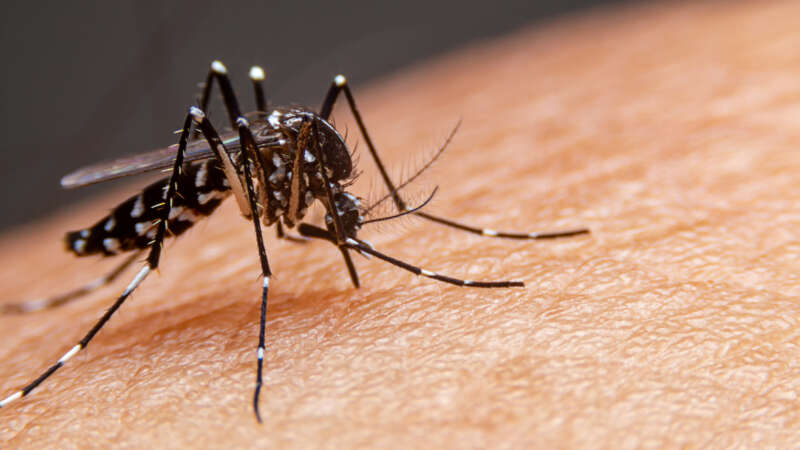
Dengue fever, once confined to the tropics, now threatens the U.S.
Climate change is expanding the habitat of the mosquitoes that carry the disease, allowing them to spread further north.
Meg Norris was traveling in Argentina in April when the first signs of dengue fever hit her. The weather in Salta, just south of the Bolivian border, was warm, but Norris, a 33-year-old from Boulder, Colorado, zipped a fleece sweatshirt around her body to stop herself from shivering.
“I thought it was sun poisoning,” she said.
How Climate Change is Spreading Malaria in Africa
Warming temperatures are chasing animals and plants to new habitats, sometimes with devastating consequences to ecosystems. But there is little evidence regarding how far and how fast the invaders might be moving.
A new study offers a glimpse of the future by looking to the past. Mosquitoes that transmit malaria in sub-Saharan Africa have moved to higher elevations by about 6.5 meters (roughly 21 feet) per year and away from the Equator by 4.7 kilometers (about three miles) per year over the past century, according to the study.
Mosquito-borne Diseases & the Environment
Climate change and human activity are enabling the spread of mosquito-borne diseases, like dengue fever, to new places. Stanford infectious disease experts and disease ecologists discuss what we know and how communities can protect themselves from these changing disease threats.
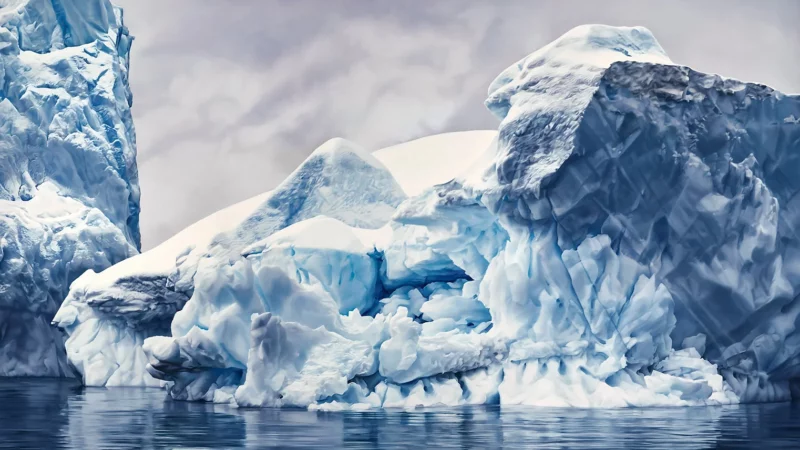
Zaria Forman: Drawing Attention to a Changing World
Zaria Forman, a contemporary artist residing in New York, creates astonishingly realistic drawings of arctic landscapes. Her extraordinary talent and methodology have gained her critical acclaim, establishing her as one of today’s most influential artists.
Forman uses her fingers and the palm of her hands almost exclusively to create her drawings of quickly disappearing glaciers and icebergs.