Disease
Japanese “Forest Medicine” – Using Nature to Heal Yourself
The fountain of youth is a forest. Trees cast off years and grant health and cheer, or so transcendentalist Ralph Waldo Emerson claimed in his 1836 essay “Nature.” ”In the woods,” he wrote, “I feel that nothing can befall me [. . .] which nature cannot repair.”
Indeed, research shows that trees really do have healing powers. For one thing, they release antimicrobial essential oils, called phytoncides, that protect trees from germs and have a host of health benefits for people.
What is Forest Bathing?
Check out this video by Cascadia Forest Therapy to discover the magical healing powers of nature.
Peter DeChant: Vector Control Visionary
The story of Peter DeChant, a veteran in the mosquito and vector control profession whose journey spans over four decades, is one of dedication, innovation, and relentless commitment to combating mosquito-borne diseases.
Peter’s journey began in 1978 when he became a field technician with Multnomah County Vector Control in Portland, Oregon. Little did he know then that this would mark the start of a lifelong crusade against one of the deadliest creatures on the planet.
By 1983, Peter’s skills and passion for his work led him to the role of Chief Sanitarian, where he led the program for 14 years. It was during this time that he honed his expertise and laid the foundation for his future endeavors.
Mosquitoes that carry West Nile are becoming resistant to insecticides
John VanDenBerg suspects he was gardening when a mosquito got him.
It was September 2018, and VanDenBerg, then 67, had been feeling a little “off” for a few days, he said, like maybe he had the flu.
But one morning, as he was walking out of his Colorado home, he collapsed.
The Economics of Resistance
It would be extremely difficult to calculate, with any high degree of accuracy, the global economic impact of insecticide resistance. For starters, we must consider that insect management plays a pivotal role in a variety of sectors – agriculture, home and garden, forestry, structural applications, and vector control. Analysis of the totality of economic impacts arising from resistance in any one of these sectors quickly becomes a complicated interplay of variables that interact within that given system.
To account for the full economic impact, one must layer in the amount being spent on insect management and how much of that investment is lost to resistance, but also the economic impact of losses to the overarching objectives of a given program.
To calculate the impact, you must first calculate what is at risk.
How Does Insecticide Resistance Happen?
Check out this video by MalariaGen focusing on how natural selection drives insecticide resistance relating to malaria.
David Goodsell: Molecular Biology Meets Artistry
David Goodsell, a distinguished American molecular biologist and illustrator, is renowned for flawlessly blending his expertise in molecular biology with an enchanting artistic flair.
Holding a Ph.D. in Molecular Biology from the University of California, Los Angeles, Goodsell’s molecular artwork graces numerous publications, textbooks, and exhibits, offering a visually stunning insight into the intricate structures of molecules, such as Ebola, Zika, Covid-19, and HIV.
Dr. Darin Detwiler: Shaping the Future of Food Safety
Dr. Darin Detwiler, LP.D., M.A.Ed., is an influential figure in the realm of food policy and technology, currently serving as the Assistant Dean of Academic and Faculty Affairs at Northeastern University’s College of Professional Studies in Boston, MA. In addition to his administrative role, Dr. Detwiler is an Assistant Teaching Professor of Food Policy and leads the MS in Regulatory Affairs of Food and Food Industry program.
With over 25 years of experience influencing federal food policy, Dr. Detwiler is a globally recognized expert in the field with his contributions extending beyond the academic sphere, as he actively engages with industry events and publications.
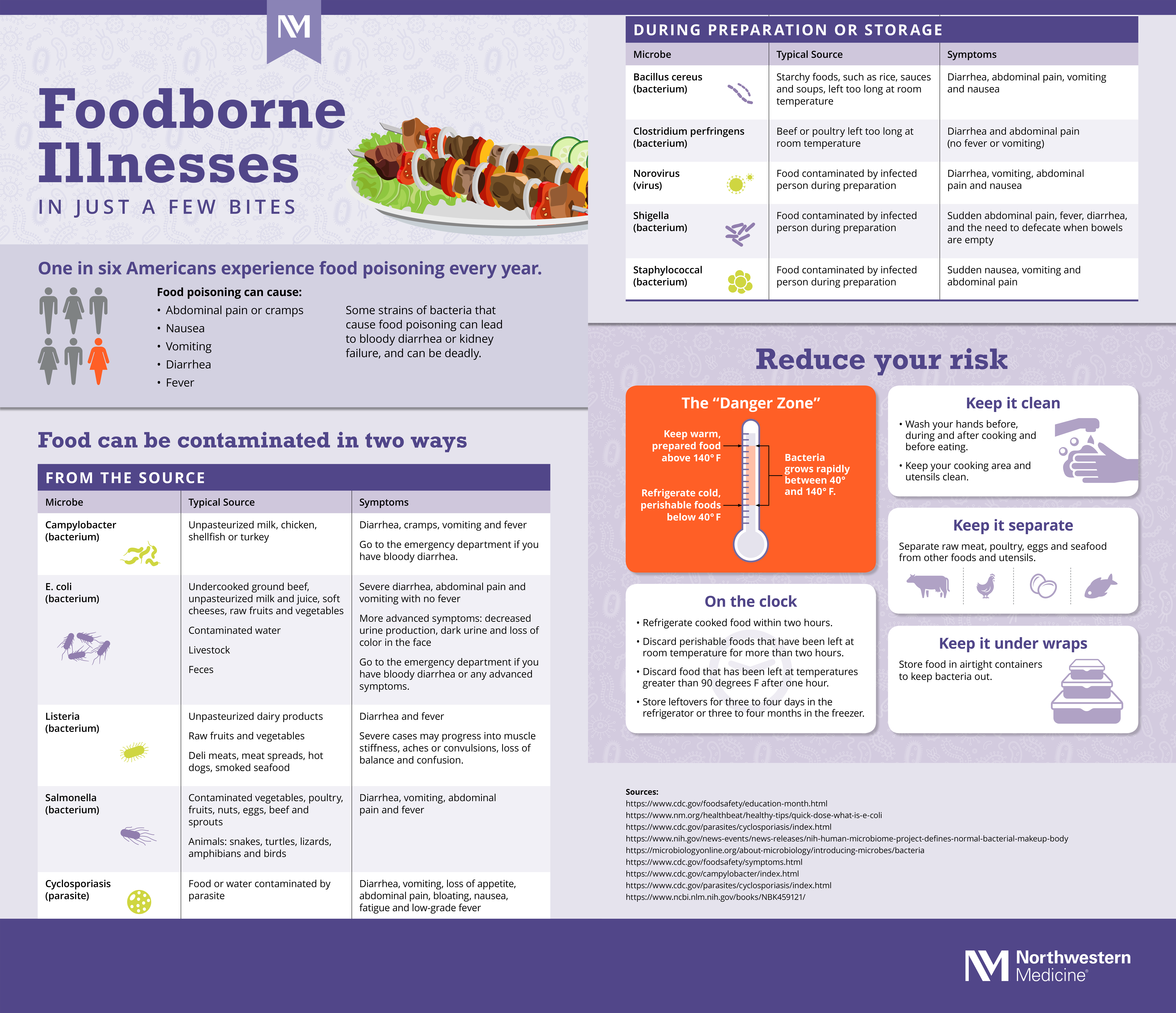
Reduce Your Risk of Foodborne Illness
Here’s what you need to know about foodborne illnesses in just a few bites.
Beyond Salmonella: Emerging Foodborne Threats
Walkerton, a serene town in Bruce County, Ontario, with a population of under 5,000, embodies tranquil rural charm, where close-knit communities thrive amid picturesque landscapes. Here on May 15, 2000, the local public utilities commission took a routine sample of the water supply and discovered E. coli contamination. The commission didn’t notify public health officials.
In the following days, several people fell ill with bloody diarrhea. The local public utilities commission reassured officials a couple of times that the water supply was safe, even though cases kept rising. By the time health officials finally warned the community against consuming untreated tap water, over 40 individuals had already sought medical attention at the hospital.
The Walkerton E. coli outbreak that saw 2,300 people fall ill, and seven die, was the worst public health disaster involving municipal water in Canadian history.