Forests
Jacques Régnière: Budworm to BioSIM
Jacques Régnière, born in Quebec City, has dedicated over four decades to advancing our understanding of forest pests and protecting our global forests. Earning his bachelor’s degree in biology from Laval University and a Ph.D. in insect ecology and biomathematics from North Carolina State University, Régnière began his career at the Canadian Forest Service in 1980, where he served until his retirement in 2024.
Throughout his distinguished career, Régnière focused on pressing issues in forest ecology, notably the population dynamics of the spruce budworm, mountain pine beetle, and spongy moth. His work in quantitative ecology has influenced pest management practices and provided a better understanding of climate change’s impact on invasive species and forest health.
Purdue launches new AI-based global forest mapping project
Purdue University’s Jingjing Liang has received a two-year, $870,000 grant from the World Resources Institute to map global forest carbon accumulation rates.
“To accurately capture the carbon accumulation rates of forested ecosystems across the world has always been a challenging task, mostly because doing so requires lots of ground-sourced data, and currently such data are very limited to the scientific community,” said Liang, an associate professor of quantitative forest ecology and co-director of the Forest Advanced Computing and Artificial Intelligence Lab.
“This task is considerably more challenging than mapping carbon emissions from forest loss,” said Nancy Harris, research director of the Land & Carbon Lab at the World Resources Institute, a nonprofit research organization based in Washington, D.C. “With emissions, there’s a clear signal in satellite imagery when trees are cut, leading to a big drop in forest carbon stocks and a relatively abrupt pulse of emissions to the atmosphere. With sequestration, forests accumulate carbon gradually and nonlinearly.”
The Role of Technology in Forest Management
In Brazil’s Pará region, new roads are cutting through the pristine Amazon rainforest, opening up once-untouched areas to human activities. Expansive stretches of lush greenery are vanishing at an alarming pace, yielding to barren patches and freshly cleared land.
Meanwhile, far into space, the European Space Agency captures high-resolution satellite images of the region that unveil an important pattern: deforestation occurs predominantly near these newly constructed roads.
Back in 2016, it sparked a question: what if there were a tool to monitor these roads and forecast potential deforestation areas? Not long after PrevisIA was born.
In 2021, Microsoft with Vale Fund and the Amazon Institute for Man and the Environment (Imazon) developed a new AI tool called PrevisIA, to predict deforestation hotspots in the Amazon. Using satellite imagery from the European Space Agency and an algorithm developed by Imazon, the tool produces heat maps showing the most exposed conservation areas, Indigenous lands, and other settlements, along with rankings for states and municipalities.
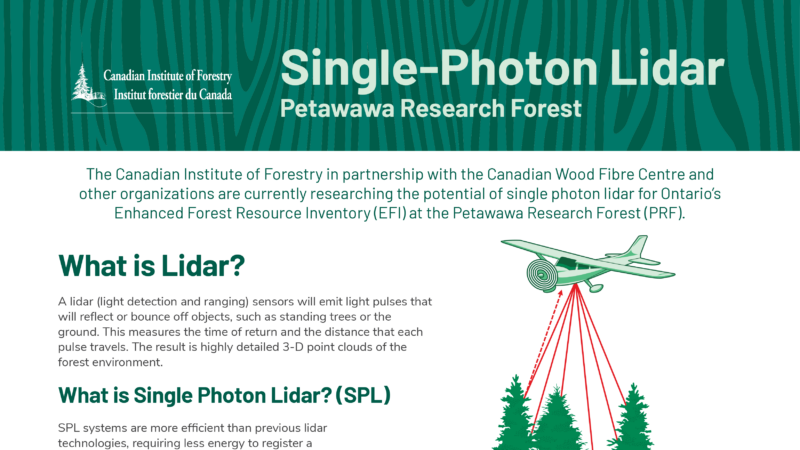
Single-Photon Lidar
The Canadian Institute of Forestry in partnership with the Canadian Wood Fibre Centre and other organizations are currently researching the potential of single photon lidar for Ontario’s
Enhanced Forest Resource Inventory (EFI) at the Petawawa Research Forest (PRF).
What is Lidar?
A lidar (light detection and ranging) sensors will emit light pulses that will reflect or bounce off objects, such as standing trees or the ground. This measures the time of return and the distance that each pulse travels. The result is highly detailed 3-D point clouds of the forest environment.
Thomas Dambo: The Master of Upcycled Urban Sculptures
Thomas Dambo, born in Odense, Denmark in 1979, grew up in a creative and communal environment. From a young age, Dambo was encouraged to explore his creativity, building his first wooden box for his brother’s pacifier and scavenging materials to construct massive fortresses with his friends.
As a teenager, Dambo delved into street art, urban exploration, and graffiti. His passion for urban culture and hip-hop led him to become a beatboxer, touring with Norwegian rapper Skranglebein. In 2004, he formed the hip-hop super crew Fler Farver with his younger brother and friends, releasing nine albums and gaining significant recognition in the Danish underground hip-hop scene.
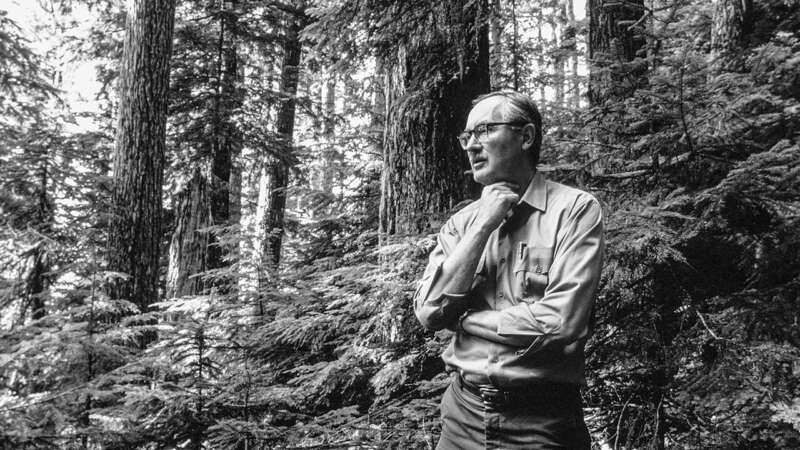
Jerry Franklin: The Father of New Forestry
Jerry Franklin, known as the “Father of New Forestry,” has made his mark in forest management for integrating ecological and economic objectives. His approaches, which faced skepticism initially, have become the standard in both environmental and timber industry circles.
Franklin began his career as a research forester for the USDA Forest Service in 1959. His early work included long-term experiments on forest ecosystems, particularly old-growth forests.
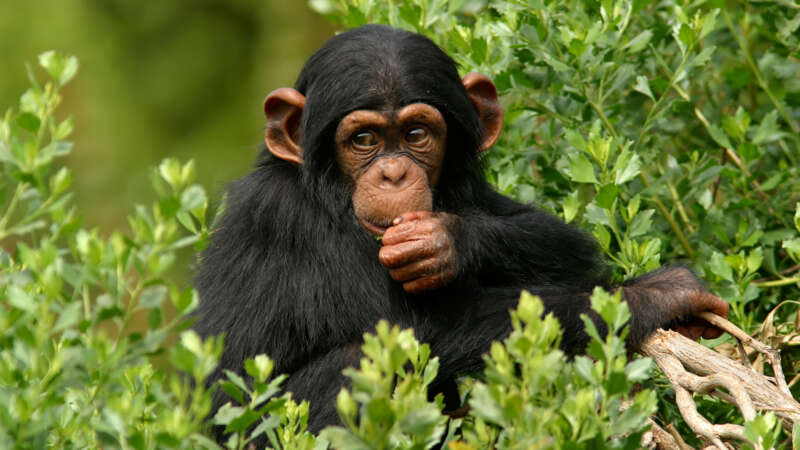
Chimpanzees May Self-Medicate With Plants, Using the Forest as a Pharmacy
Chimpanzees may be using the forest like their own personal pharmacy. When they’re sick, the primates appear to seek out and eat plants with antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, according to new research.
Observers have long suspected that chimpanzees use plants to self-medicate. Now, a new paper published last week in the journal PLOS ONE offers more evidence in support of this idea.
Researchers followed two groups of wild chimpanzees through Uganda’s Budongo Forest for eight months. They recorded what the animals ate, as well as whether they were sick—which they determined by checking their feces for parasites, testing their urine for elevated levels of immune cells and looking for wounds.
Shrinking Forests, Emerging Diseases
Dona Dora’s man is away from home a lot more these days. It didn’t used to be like that.
He leaves early, sometimes on foot, but increasingly on his bicycle, and heads into the forests surrounding Belém, the capital of Brazil’s Para province. He keeps his eyes open especially for five medicinal plants that are always in demand — sucuúba (Himatanthus sucuuba), copaíba (Copaifera spp.), andiroba (Carapa guianensis), barbatimão (Stryphnodendron spp.) and pãu d’arco (Tabebuia avellanedae).
Fifteen years earlier, he would have found all five within hours and been back for lunch, but times have changed. These days, medicinal forest plants in high demand are becoming harder to find as forests that have stood strong for millennia are cleared to make way for grazing pastures for millions of cattle, agriculture, and development.
Now, Dona Dora’s man can spend a whole day and not find more than a few plants. It might be late at night before he gets back home.
What is a Healthy Forest?
Healthy forests are beneficial for people and wildlife.
When forests are healthy, they produce enough food, water and shelter to support local wildlife, clean the air, reduce erosion into nearby streams and lakes, and are less susceptible to large-scale high-severity wildfires.
But what does a healthy forest look like?
Summer Lajoie: The Simplicity of Creation
Summer Lajoie merges artistry with nature, creating ephemeral art that captures the fleeting beauty of the natural world. Each creation reflects a moment of profound connection and presence.
For Summer, art is more than just a form of expression; it’s a vital ritual. Inspired by the transient works of Andy Goldsworthy, she engages with the environment, crafting art from the elements she encounters. This process focuses less on the final product and more on the act of creation itself.