ebola
A Shining New Age of Vaccines
With vaccines, history repeats itself like music stuck in a loop. On the one hand, advancing technologies create vaccines against a growing list of lethal diseases and conditions. On the other hand, outrageous myths and conspiracy theories compete against science. Familiar and strong emotions run the gamut, from relief when deadly diseases like smallpox are eradicated to anger about perceived dangers to health, governmental overreach and threats to freedom of choice. While religious, commercial, pseudo-scientific and political interests cash in on the confusion, context and meaning are sometimes lost or forgotten. Telling facts apart from misinformation becomes difficult.
Understanding how vaccines are evolving can help better understand both why they are one of medical science’s supreme triumphs and also why the anti-vaccine movement continues to grow and influence so many.
Shrinking Forests, Emerging Diseases
Dona Dora’s man is away from home a lot more these days. It didn’t used to be like that.
He leaves early, sometimes on foot, but increasingly on his bicycle, and heads into the forests surrounding Belém, the capital of Brazil’s Para province. He keeps his eyes open especially for five medicinal plants that are always in demand — sucuúba (Himatanthus sucuuba), copaíba (Copaifera spp.), andiroba (Carapa guianensis), barbatimão (Stryphnodendron spp.) and pãu d’arco (Tabebuia avellanedae).
Fifteen years earlier, he would have found all five within hours and been back for lunch, but times have changed. These days, medicinal forest plants in high demand are becoming harder to find as forests that have stood strong for millennia are cleared to make way for grazing pastures for millions of cattle, agriculture, and development.
Now, Dona Dora’s man can spend a whole day and not find more than a few plants. It might be late at night before he gets back home.
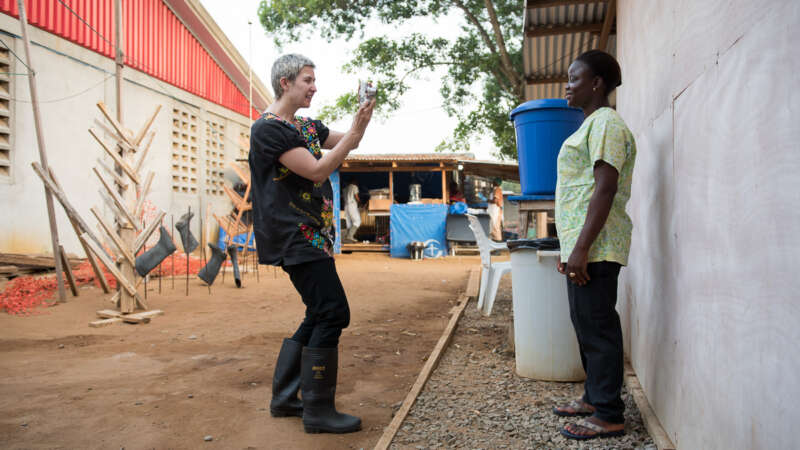
Mary Beth Heffernan: From the Studio to the Hospital Ward
Mary Beth Heffernan, a Los Angeles based artist, brings together corporeality and imagery through various media. Her work examines deep questions about how bodies and their experiences are represented in digital and physical forms.
One of Heffernan’s most notable projects, the PPE Portrait Project, began in 2014 to humanize the protective gear of Ebola workers in Liberia. By placing portraits on protective equipment, the project helped mitigate fear and foster connections between healthcare workers and patients. The initiative gained international attention and was adapted for COVID-19 response, impacting healthcare settings worldwide, including major institutions like Stanford Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital.
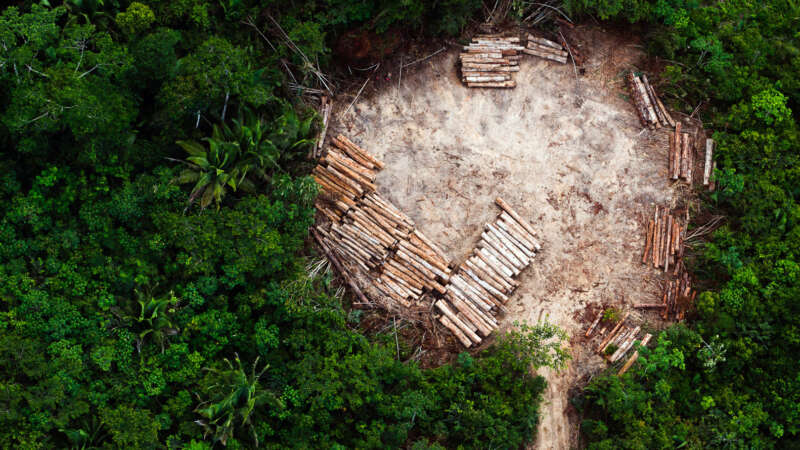
Deforestation’s Hidden Toll: Amplifying Disease Risk Worldwide
In the last couple of decades, the lush rainforest around the remote village of Meliandou in the heart of Guinea has become patchier. Animals, like bats, saw their habitats dwindle and in a quest for survival, they sought refuge in closer proximity to human environments, making the boundaries between species thinner. A hollowed-out tree in the middle of the village became home to a colony of bats.
About 50 meters from the same tree, in the heart of Meliandou, a two-year-old boy named Emile lived with his family. In a matter of days, Emile fell ill with an unknown virus, developed a high fever, and died. Soon the same virus, that scientists now believe Emile got from the bats, took the lives of his sister, mother, and grandmother. The village, surrounded by a ring of forest, unexpectedly became the epicenter of a devastating outbreak that would leave an indelible mark.